Are you curious about the key differences between adenomyosis and endometriosis? These two conditions might sound similar, but they affect the female reproductive system differently. Adenomyosis involves the invasion of endometrial tissue into the uterine wall, while endometriosis sees this tissue implanting itself on various pelvic organs, leading to different sets of symptoms and treatment approaches.
We’re here to unravel adenomyosis vs. endometriosis, helping you understand their unique characteristics, symptoms, and treatments. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge to navigate these conditions confidently and make informed decisions about your health. So, let’s dive in and uncover the important differences between adenomyosis and endometriosis.
Adenomyosis vs. Endometriosis: Understanding the Differences
When it comes to adenomyosis vs. endometriosis, it’s essential to grasp the differences between these two conditions. Both involve the presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus, leading to a range of symptoms, particularly pelvic pain. However, the devil is in the details, and understanding the nuances can be vital for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Adenomyosis and Endometriosis: A Common Connection
Both adenomyosis and endometriosis share the common thread of endometrial tissue behaving abnormally outside the uterus. However, their locations and implications differ. Adenomyosis involves the invasion of endometrial tissue into the uterine wall, causing uterine muscle thickening. Endometriosis sees this tissue implanting itself on various pelvic organs like the fallopian tubes, causing scar tissue and chronic pain.
Diagnosing Adenomyosis and Endometriosis
Accurate diagnosis is critical, as symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, severe pelvic pain, and painful periods can overlap between adenomyosis and endometriosis. Healthcare providers employ various methods, including imaging, prior uterine surgeries, and hormonal treatments, to distinguish between the two.
Treatment Options: Adenomyosis and Endometriosis
Treatment strategies for adenomyosis and endometriosis vary based on the severity of symptoms and personal preferences. Hormonal medications, hormonal contraceptives, and uterine artery embolisation are among the options to alleviate pain and control abnormal tissue growth. In severe cases, hysterectomy and removal of the uterus might be recommended for adenomyosis, while laparoscopic surgery is a common approach for endometriosis.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Recognising the risk factors and symptoms associated with adenomyosis and endometriosis can lead to early diagnosis and intervention. Addressing these conditions promptly can help manage heavy bleeding, chronic pain, and other distressing menstrual cycle-related issues.
So, while adenomyosis and endometriosis may share similarities in their involvement with endometrial tissue, understanding their differences is essential for proper diagnosis and tailored treatment. If you’re experiencing pelvic pain, abnormal menstrual bleeding, or other concerning symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional to explore your options and find relief from these conditions.
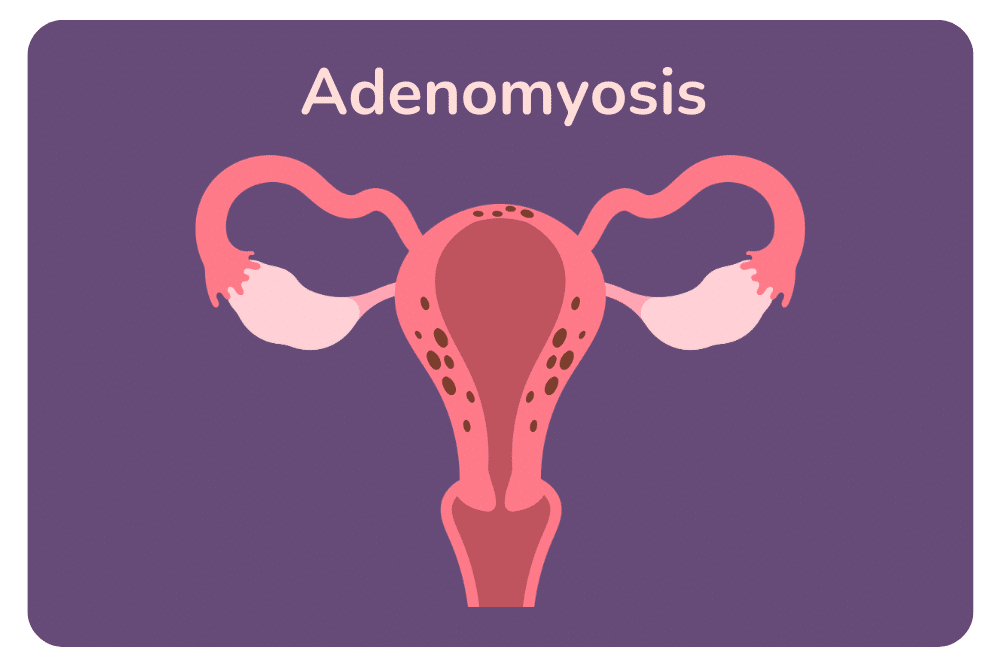
Is Adenomyosis Worse Than Endometriosis?
When it comes to adenomyosis vs. endometriosis, many individuals wonder if one condition is worse than the other. The answer to this question isn’t a straightforward “yes” or “no,” as the severity of these conditions can vary significantly from person to person. Let’s explore some key factors to consider when comparing adenomyosis and endometriosis.
Symptom Severity
Both adenomyosis and endometriosis can cause a range of symptoms, including pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, and painful periods. The severity of these symptoms can be influenced by factors such as the extent of tissue involvement, individual pain threshold, and the presence of other health conditions. Some individuals with adenomyosis may experience milder symptoms, while others with endometriosis may have more severe pain.
Impact on Fertility
Endometriosis is often associated with a higher risk of fertility problems due to the formation of scar tissue and adhesions that can affect the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Adenomyosis, on the other hand, may also impact fertility but tends to do so less frequently. However, both conditions can make it challenging for some individuals to conceive.
Personal Experience
Whether adenomyosis or endometriosis feels “worse” is a highly personal experience. Some individuals with adenomyosis may find their symptoms more debilitating, while others with endometriosis may have a more challenging journey. It’s important to remember that pain and discomfort are subjective, and what matters most is how these conditions affect your quality of life and overall well-being.
There’s no definitive answer to whether adenomyosis is worse than endometriosis. Both conditions can be challenging to live with, and their impact can vary widely among individuals. If you suspect you have either condition or are experiencing concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalised treatment plan.
Can Endometriosis be Misdiagnosed as Adenomyosis?
The diagnostic journey of pelvic pain and menstrual irregularities can sometimes be a complex and confusing one. One common question that arises is whether endometriosis can be misdiagnosed as adenomyosis or vice versa.
The fact is that endometriosis can indeed be misdiagnosed as adenomyosis and vice versa due to their similar symptoms and the fact that they often coexist. Both conditions involve the abnormal growth of tissue outside the uterus, leading to symptoms like pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, and fertility issues.
Accurate differentiation can be challenging, as they may share overlapping clinical features and require advanced diagnostic techniques, such as laparoscopy and imaging studies, for definitive diagnosis. Therefore, a thorough evaluation by a skilled healthcare provider is crucial to distinguish between the two conditions and provide appropriate treatment options tailored to the patient’s specific diagnosis and needs.
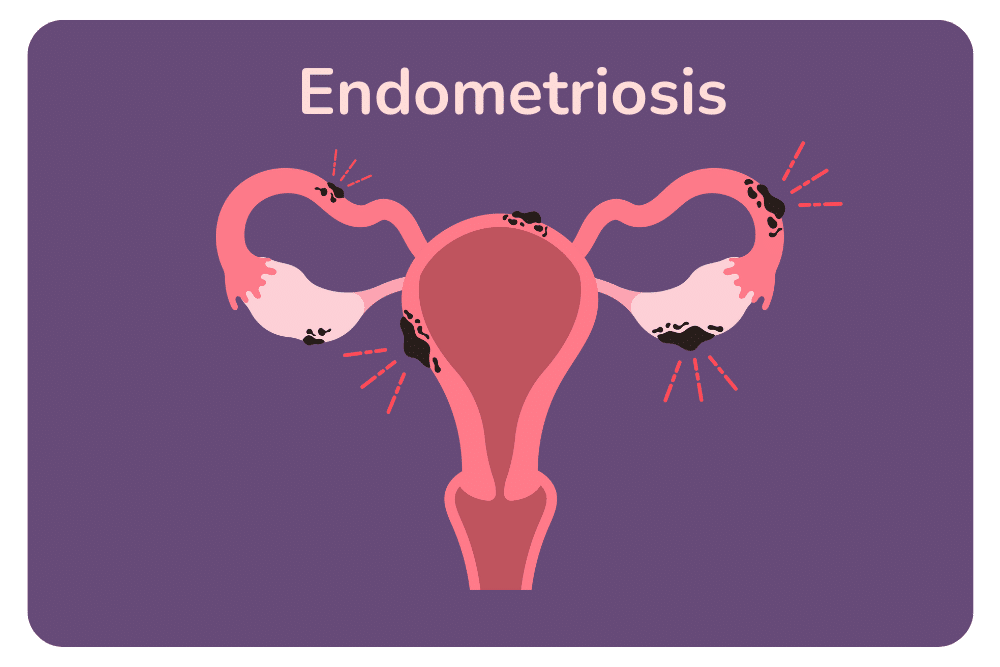
Adenomyosis and Endometriosis Treatment Options
Managing endometriosis and adenomyosis symptoms effectively requires a tailored approach that takes into account the severity of your symptoms, your overall health, and your future reproductive goals. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to help alleviate pain, control abnormal tissue growth, and improve quality of life.
Hormonal Medications
Hormonal medications are often the first line of defence against both adenomyosis and endometriosis. These medications aim to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce the growth of endometrial tissue. Common hormonal treatments include birth control pills, hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs), and progestin-only therapies. These can help manage symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and painful menstrual periods.
Pain Relief Measures
Over-the-counter pain relievers can provide temporary relief from the pain associated with adenomyosis and endometriosis. However, they do not address the underlying causes of these conditions and are usually used in conjunction with other treatments.
Laparoscopic Surgery
For individuals with severe symptoms or complications related to endometriosis, laparoscopic surgery may be recommended. During this minimally invasive procedure, a surgeon removes or destroys abnormal tissue growth, adhesions, and cysts. It can provide significant relief and may improve fertility for those trying to conceive.
Uterine Artery Embolisation (UAE)
Uterine artery embolisation is a non-surgical option for treating adenomyosis. In this procedure, tiny particles are injected into the arteries that supply blood to the uterus, reducing blood flow to the affected tissue and shrinking the adenomyosis. UAE can alleviate symptoms such as heavy bleeding and pelvic pain.
Endometrial Ablation
Endometrial ablation is a procedure that removes the uterine lining. It is typically used for individuals with adenomyosis or endometriosis-related bleeding disorders who do not wish to preserve their fertility. This procedure can significantly reduce or eliminate heavy menstrual bleeding.
Hysterectomy
In cases of severe adenomyosis or endometriosis that do not respond to other treatments and when fertility preservation is not a concern, a hysterectomy may be recommended. This surgical procedure involves the removal of the uterus and is considered a definitive solution.
Hormonal Treatments
Specific hormonal treatments can induce a temporary menopausal state (what is menopause?), suppressing hormone production and reducing the growth of endometrial tissue. These treatments are typically used for short periods and can help alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications
Some individuals find relief from adenomyosis and endometriosis symptoms by making lifestyle and dietary changes. These may include adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, managing stress with mindfulness techniques, exercising regularly, and incorporating alternative therapies like acupuncture or yoga.
The choice of treatment for adenomyosis and endometriosis depends on individual circumstances, including the severity of symptoms, fertility goals, and overall health. Consult with a healthcare provider who specialises in reproductive health to discuss your options and create a personalised treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and preferences.









