Wondering about bleeding during early pregnancy? Let’s talk about implantation bleeding, a sign that a fertilised egg is attaching to the uterus lining. If you want to know the answer to “When does implantation bleeding happen?” Well, it usually occurs about 6 to 12 days after getting pregnant, around a week before your expected period.
The journey from conception to pregnancy involves the fertilised egg turning into a blastocyst and moving into the uterus. This little guy then latches onto the uterine lining, causing some tiny blood vessels to break, resulting in what we call implantation bleeding.
Here’s the deal: this bleeding is like a sign that pregnancy might be happening. Most women experience it around 10 to 14 days after getting pregnant, but keep in mind, everyone’s different. So, if you suspect pregnancy and notice some light pink or brownish discharge, along with mild cramps, it might be implantation bleeding.
Stay tuned as we dive deeper into the specifics of when implantation bleeding typically occurs. Understanding this can be pretty helpful if you’re on the path to pregnancy.
How Do I Know If It’s Implantation Bleeding?
Identifying implantation bleeding can be challenging, as it shares some similarities with other types of vaginal bleeding. However, there are a few characteristics that may help you distinguish it from other forms of bleeding:
Timing
Implantation bleeding typically occurs about 6 to 12 days after conception, roughly a week before your expected period. This timing aligns with the embryo’s attempt to attach to the uterine lining.
Colour and Amount
Implantation is usually scanty and light bleeding, not resembling regular menstrual bleeding. The blood may appear as a light pink or brownish discharge. It’s generally not heavy enough to require a pad or tampon.
Duration
Unlike a menstrual period, which can last several days, implantation bleeding is often brief, lasting for a few hours to a few days.
Associated Symptoms
Some women may experience mild cramping along with implantation bleeding, but it is usually less intense than menstrual cramps.
Consistency with Other Symptoms
If you’ve been trying to conceive and notice other early pregnancy symptoms, such as breast tenderness, nausea, or changes in appetite, these may complement the possibility of implantation bleeding.
It’s important to note that not all women experience implantation bleeding. If you’re uncertain about the cause of vaginal bleeding or if you suspect you might be pregnant, consider taking a home pregnancy test or consulting a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance based on your situation and help confirm whether you’re pregnant or if there’s another reason for the bleeding.
How Long After Conception Does Implantation Happen?
Implantation typically occurs about 6 to 12 days after conception. Here’s a breakdown of the timeline:
Fertilisation
Conception occurs when a sperm fertilises an egg. This typically happens in the fallopian tube.
Formation of Blastocyst
After fertilisation, the fertilised egg, now called a zygote, undergoes several cell divisions and becomes a blastocyst.
Journey to the Uterus
The blastocyst travels down the fallopian tube toward the uterus.
Implantation
Once in the uterus, the blastocyst seeks to attach itself to the lining of the uterus. This process, known as implantation, involves burrowing the blastocyst into the endometrial tissue.
The implantation process usually occurs around 6 to 12 days after conception, although the timing can vary among women. After successful implantation, the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) begins to be produced, and this is what is detected by pregnancy tests.
Keep in mind that these are average timeframes, and individual variations are common. If you suspect you might be pregnant or are trying to conceive, understanding this timeline can help you recognise the potential signs and symptoms associated with early pregnancy.
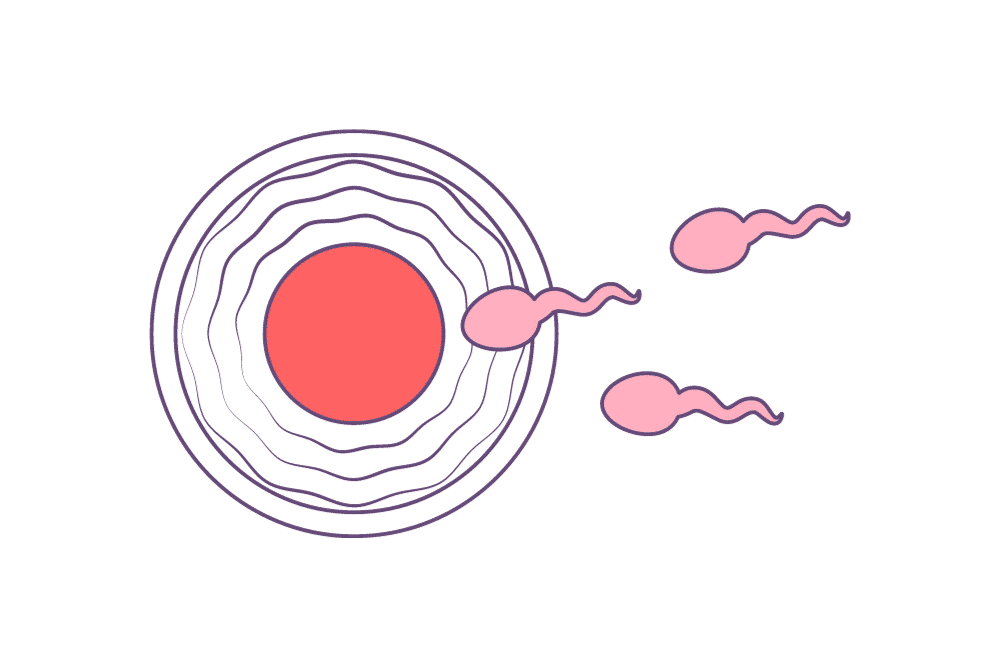
How Many Weeks Pregnant Are You After Experiencing Implantation Bleeding?
If a woman experiences implantation bleeding, it’s usually considered an early sign of pregnancy. Implantation bleeding typically occurs around 6 to 12 days after conception. At this stage, a woman is generally in the very early weeks of pregnancy.
Pregnancy is typically counted from the first day of the woman’s last menstrual period (LMP), so by the time implantation bleeding occurs, she may be around 2 to 4 weeks pregnant. However, remember that conception time (when the sperm fertilises the egg) occurs a bit later, usually around the middle of the menstrual cycle.
If you suspect you might be pregnant after experiencing implantation bleeding, it’s a good idea to take a home pregnancy test a few days after the bleeding has occurred or consult a healthcare professional for confirmation and guidance. They can provide more accurate information based on your circumstances.
How Many Days After Implantation Can You Take a Pregnancy Test?
After implantation, it takes some time for the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to build up to levels that a pregnancy test can detect. In general, it’s advised to wait at least a few days to a week after implantation before taking a home pregnancy test for more accurate results.
Most home pregnancy tests claim to provide accurate results on the first day of a missed period, but some tests are more sensitive and can detect pregnancy earlier. However, the accuracy of the test increases the closer you get to the day of your expected period.
If you’ve experienced implantation bleeding, you should wait a few days after the bleeding occurs to allow hCG levels to rise. Testing too early can result in a false-negative result because the hormone levels might not be high enough for detection.
If you’re eager to confirm a pregnancy, it’s a good idea to follow the instructions on the pregnancy test kit and consider testing around the time of your expected period or a few days afterwards. If you get a negative result but still suspect you might be pregnant, you can retest after a few days or consult a healthcare professional for further guidance.

What Are the 4 Stages of Implantation?
Implantation is a complex process that occurs in several stages as the fertilised egg, or blastocyst attaches itself to the uterine lining. The four stages of implantation are as follows:
1. Apposition
This is the initial contact between the blastocyst and the uterine lining. The blastocyst starts to get close to the endometrial surface.
2. Adhesion
During this stage, the blastocyst adheres to the uterine lining. Specialised cells on the surface of the blastocyst interact with the cells of the endometrium, allowing the blastocyst to attach more firmly.
3. Invasion or Penetration
The blastocyst begins to penetrate the endometrial lining. This process involves the blastocyst cells breaking through the uterus’s epithelial layer and burrowing into the underlying tissue.
4. Decidualisation
Once the blastocyst has successfully implanted, the surrounding endometrial cells undergo changes to support the developing embryo. This process, decidualisation, creates a supportive environment for the early stages of pregnancy.
These stages are vital for establishing a successful pregnancy, and any disruptions in this process can impact implantation and subsequent development. Remember that each stage’s exact timing and details can vary among women.
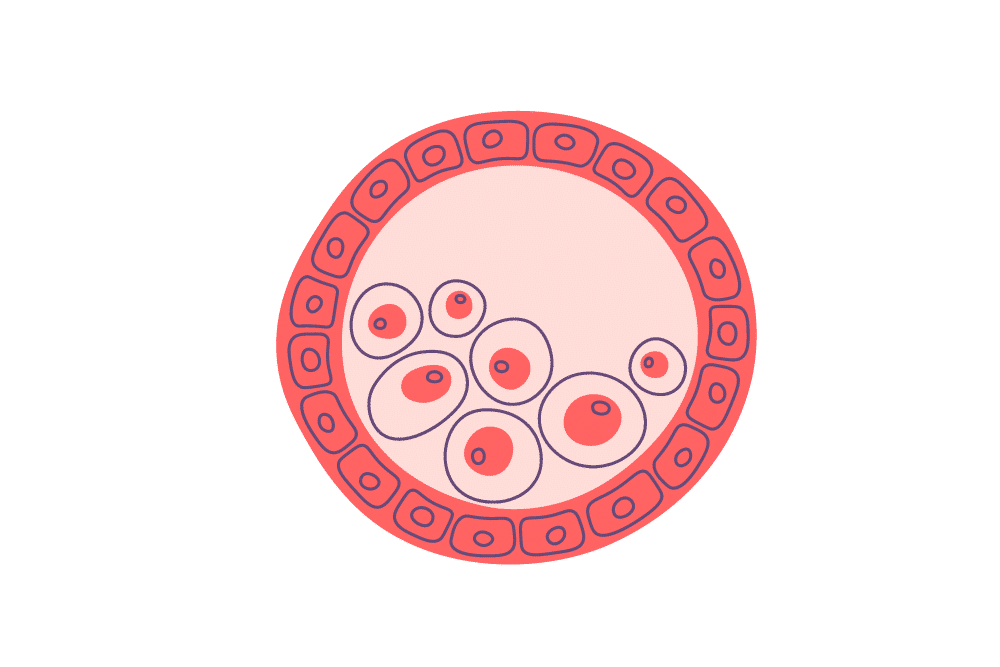
How to Tell the Difference Between Implantation Bleeding and a Period?
It can be tricky to tell the difference between implantation bleeding and a regular period. Implantation bleeding, which happens 6 to 12 days after conception, is usually lighter and shorter than a typical period, often appearing as light pink or brown discharge without needing a lot of sanitary products.
On the other hand, a regular period is heavier, lasts several days, and comes with stronger cramps and other typical menstrual symptoms. If you’re unsure, considering the timing, flow, and accompanying symptoms can help. However, taking a home pregnancy test or talking to a healthcare professional for personalised advice is a good idea.